Exergaming at Home
Usability and feasibility of a newly developed step-based exergame device (Dividat SensoFlex) for home use for healthy older adults
The degenerative changes associated with aging cause an increased risk of falls in elderly. Falls are a leading cause for injuries, reduced mobility and independency as well as decreased well-being. In daily life, not only need sensory and motor but also cognitive functions are required, whereas a strong need for combined cognitive-motor training exists, especially in falls prevention. Exergames, which require physical activity to play the game, are a promising option for cognitive-motor training.
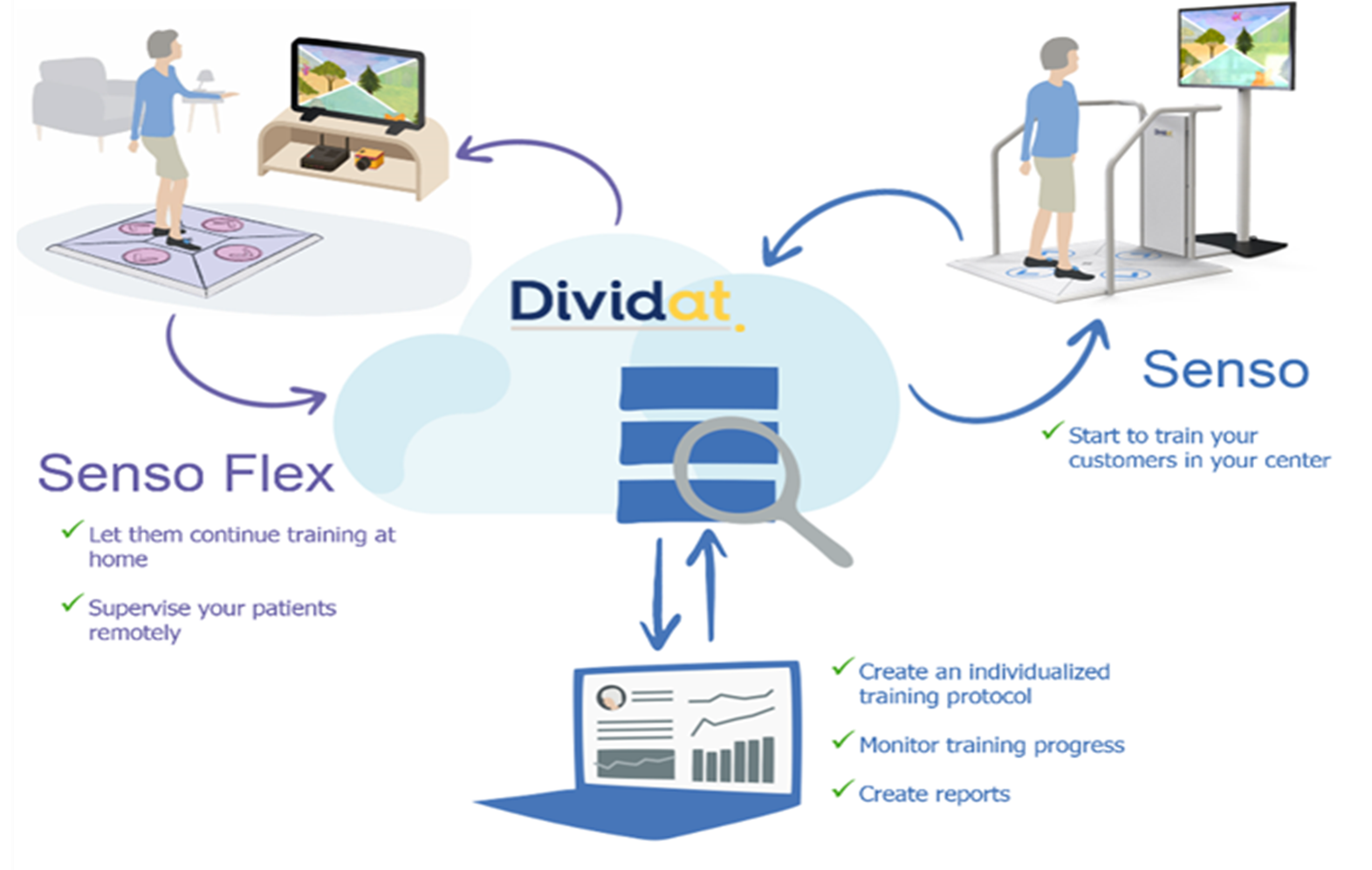
A newly developed device (Dividat SensoFlex) aims to bring the exergame experience of the already existing Dividat Senso (Dividat AG; Schindellegi; Switzerland; CE Certification) into a home-based environment. General training principles are applied as providing real-time feedback and optimal load of task demands, as well as automatized progression of difficulty level, adapted to the users' abilities.
As an important step during the development process of a new (technological) system, a usability and feasibility study helps to determine the further necessary steps and serves as a basis for following larger studies. The acceptance of exergames in elderly people has been reported not to depend only on the perception of fun while playing the game, but more on the perceived usefulness. This study aims therefore to determine the usability and feasibility of the newly developed in-home exergame and to explore potential training effects on physical and cognitive functions.
The study is planned for healthy (self-reported) older adults aged 65 and older. The intervention contains a maximum of 18 sessions (30min per session, 3x/week, 6 weeks of training). After completing the six-week training period, participants will evaluate the usability and report their game experience. In terms of evaluation of the feasibility, adherence and attrition rates will be calculated at the end of the study. Before, after six weeks, as well as after 12 weeks, physical and cognitive functions are tested. The findings of this study will help to improve the current version of the exergame and to design further trials with the end goal of providing a usable, feasible and effective training at home.
This study is a collaboration of our research group with the company external page Dividat.